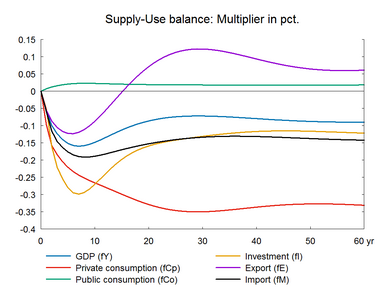
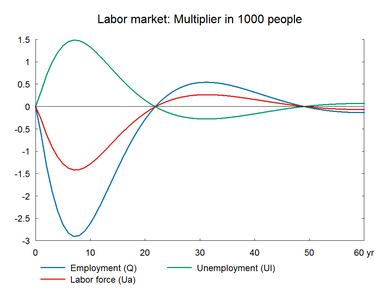
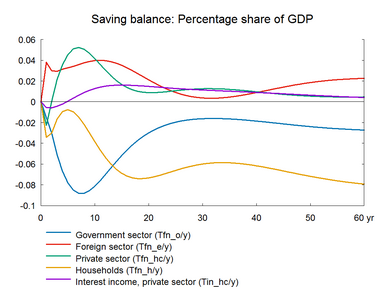
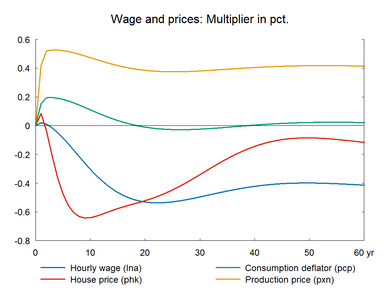
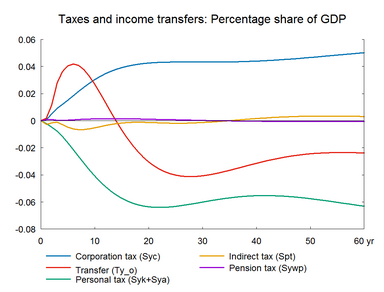
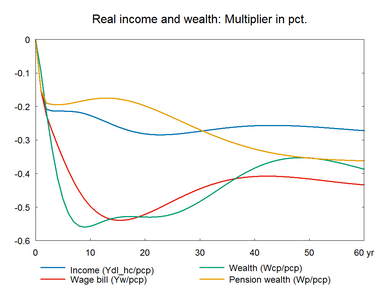
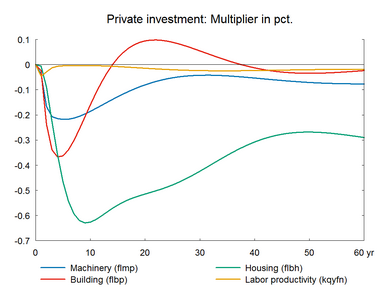
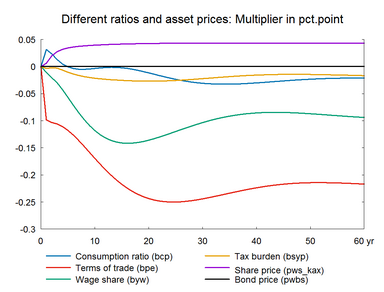
In this experiment we increase the market prices of oil permanently. The experiment has a lot of similarity with the previous experiment on foreign prices. Change in world oil prices affects all countries in the world and hence foreign markets and foreign prices will be affected. However, the experiment here does not take the international spillover into account.
The experiment presents the effect of a permanent 10 percent increase in world market oil prices.(See experiment)
Table 9. The effect of a permanent increase in world market oil prices
| 1. yr | 2. yr | 3. yr | 4. yr | 5. yr | 10. yr | 15. yr | 20. yr | 25. yr | 30. yr | ||
| Million 2010-Dkr. | |||||||||||
| Priv. consumption | fCp | -898 | -1481 | -1752 | -1979 | -2167 | -2812 | -3406 | -4035 | -4578 | -4983 |
| Pub. consumption | fCo | 36 | 63 | 83 | 100 | 112 | 132 | 129 | 130 | 136 | 144 |
| Investment | fI | -232 | -699 | -1003 | -1184 | -1330 | -1396 | -1106 | -957 | -922 | -918 |
| Export | fE | -611 | -977 | -1205 | -1362 | -1454 | -1116 | -42 | 1056 | 1800 | 2109 |
| Import | fM | -584 | -1192 | -1567 | -1808 | -2002 | -2363 | -2306 | -2234 | -2218 | -2269 |
| GDP | fY | -1137 | -1988 | -2484 | -2848 | -3111 | -3256 | -2654 | -2193 | -2034 | -2123 |
| 1000 Persons | |||||||||||
| Employment | Q | -0.61 | -1.33 | -1.89 | -2.32 | -2.64 | -2.61 | -1.38 | -0.29 | 0.33 | 0.54 |
| Unemployment | Ul | 0.34 | 0.70 | 0.98 | 1.20 | 1.36 | 1.33 | 0.69 | 0.14 | -0.17 | -0.28 |
| Percent of GDP | |||||||||||
| Pub. budget balance | Tfn_o/Y | -0.02 | -0.03 | -0.05 | -0.07 | -0.08 | -0.08 | -0.05 | -0.03 | -0.02 | -0.02 |
| Priv. saving surplus | Tfn_hc/Y | -0.02 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Balance of payments | Enl/Y | -0.04 | -0.03 | -0.03 | -0.03 | -0.03 | -0.04 | -0.04 | -0.02 | -0.01 | 0.00 |
| Foreign receivables | Wnnb_e/Y | -0.05 | -0.06 | -0.06 | -0.06 | -0.05 | -0.09 | -0.17 | -0.24 | -0.26 | -0.26 |
| Bond debt | Wbd_os_z/Y | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.56 | 0.75 | 0.79 | 0.76 | 0.72 |
| Percent | |||||||||||
| Capital intensity | fKn/fX | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.01 | -0.08 | -0.13 | -0.15 | -0.16 |
| Labour intensity | hq/fX | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| User cost | uim | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.04 | -0.02 | -0.07 | -0.11 | -0.11 | -0.11 |
| Wage | lna | 0.02 | 0.01 | -0.01 | -0.05 | -0.08 | -0.30 | -0.46 | -0.53 | -0.53 | -0.50 |
| Consumption price | pcp | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.04 | -0.01 | -0.03 | -0.02 |
| Terms of trade | bpe | -0.10 | -0.10 | -0.11 | -0.11 | -0.12 | -0.17 | -0.22 | -0.25 | -0.25 | -0.25 |
| Percentage-point | |||||||||||
| Consumption ratio | bcp | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -0.01 | -0.02 | -0.03 |
| Wage share | byw | -0.01 | -0.02 | -0.03 | -0.04 | -0.06 | -0.12 | -0.14 | -0.14 | -0.12 | -0.10 |
The increase in oil prices raises expenditure on energy imports, and the balance of payments deteriorates immediately. Nevertheless, energy exports also increase and offset most of the negative effect on the balance of payments. The public budget improves in the short run because higher oil prices mean higher taxable profits in the hydrocarbon-extracting industry.
The increase in energy price affects the general price level, and the accompanying fall in real income reduces consumption and economic activity. In the medium run, the higher unemployment reduces wages and increases competitiveness, so the period of contraction is followed by a period of expansion in employment and production.
The long-term effect on employment is zero like in the previous demand shock experiments. Thus, the increase in oil prices also represents a shock to the supply side of the international economy but it does not constitute a permanent supply shock to the employment. The long-term effect on GDP is negative partly due to the substitution effect of the permanent fall in the relative price of labor, and partly due to the permanent fall in private consumption, which triggers a fall in the content of indirect taxes in GDP. In general, the higher oil price works as a negative demand shock in the short run, and in the long run it works as a supply shock as relative factor prices change in the long run. The higher public revenues can be used to increase e.g. private consumption. Higher consumption would reduce the negative impact on wages and the positive impact on exports.
Figure 9. The effect of a permanent increase in world market oil prices