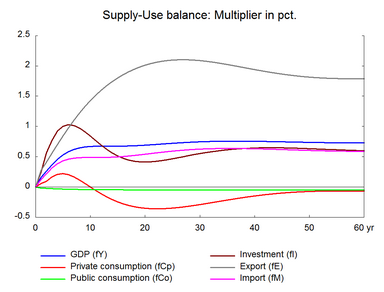
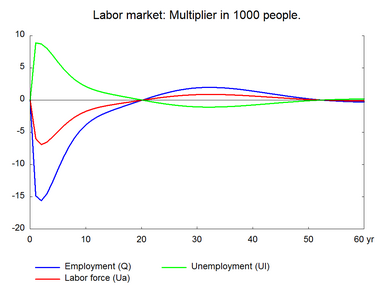
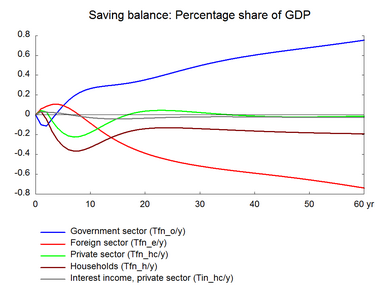
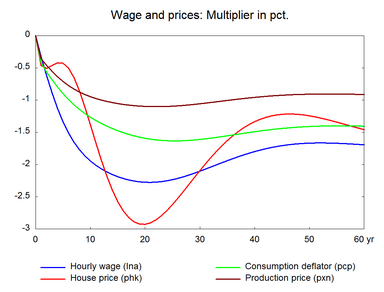
Increasing the efficiency of labor increases the supply of labor measured in efficiency units. An increase in labor efficiency reduces the demand for labor to produce a given output, and it also reduces the demand for other factors through substitution effects. Table 12 presents the effect of a permanent 1 per cent increase in labor efficiency. (See experiment)
Table 12. The effect of a permanent increase in labor efficiency
| 1. yr | 2. yr | 3. yr | 4. yr | 5. yr | 10. yr | 15. yr | 20. yr | 25. yr | 30. yr | ||
| Million 2005-kr. | |||||||||||
| Priv. consumption | fCp | 483 | 798 | 1424 | 1810 | 1936 | 6 | -2491 | -3831 | -4092 | -3675 |
| Pub. consumption | fCo | -70 | -91 | -113 | -132 | -148 | -198 | -229 | -261 | -295 | -323 |
| Investment | fI | 843 | 1909 | 2700 | 3314 | 3662 | 3345 | 2206 | 1914 | 2329 | 2977 |
| Export | fE | 2446 | 3744 | 5163 | 6563 | 7995 | 14588 | 19840 | 23865 | 26791 | 28743 |
| Import | fM | 1077 | 1940 | 2863 | 3573 | 4077 | 4994 | 5485 | 6430 | 7577 | 8624 |
| GDP | fY | 2544 | 4250 | 6011 | 7590 | 8904 | 12116 | 13158 | 14515 | 16342 | 18211 |
| 1000 Persons | |||||||||||
| Employment | Q | -14.85 | -15.61 | -14.55 | -12.74 | -10.74 | -3.85 | -1.51 | -0.05 | 1.22 | 1.90 |
| Unemployment | Ul | 8.86 | 8.70 | 8.02 | 6.99 | 5.87 | 2.10 | 0.82 | 0.02 | -0.69 | -1.06 |
| Percent of GDP | |||||||||||
| Pub. budget balance | Tfn_o/Y | -0.10 | -0.11 | -0.04 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.42 | 0.50 |
| Priv. saving surplus | Tfn_hc/Y | 0.04 | 0.03 | -0.06 | -0.13 | -0.18 | -0.18 | -0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| Balance of payments | Enl/Y | -0.06 | -0.09 | -0.10 | -0.11 | -0.09 | 0.09 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.47 | 0.52 |
| Foreign receivables | Wnnb_e/Y | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.40 | 1.39 | 2.83 | 4.43 | 6.06 |
| Bond debt | Wbd_os_z/Y | 0.29 | 0.42 | 0.46 | 0.44 | 0.35 | -0.62 | -1.85 | -3.12 | -4.50 | -5.98 |
| Percent | |||||||||||
| Capital intensity | fKn/fX | -0.19 | -0.29 | -0.37 | -0.43 | -0.47 | -0.51 | -0.53 | -0.61 | -0.68 | -0.70 |
| Labour intensity | hq/fX | -0.73 | -0.89 | -0.97 | -1.01 | -1.03 | -1.02 | -1.00 | -0.99 | -0.99 | -0.98 |
| User cost | uim | -0.41 | -0.52 | -0.61 | -0.69 | -0.76 | -0.99 | -1.11 | -1.16 | -1.15 | -1.11 |
| Wage | lna | -0.33 | -0.62 | -0.89 | -1.13 | -1.34 | -1.94 | -2.19 | -2.27 | -2.23 | -2.10 |
| Consumption price | pcp | -0.42 | -0.56 | -0.68 | -0.80 | -0.90 | -1.27 | -1.48 | -1.59 | -1.63 | -1.61 |
| Terms of trade | bpe | -0.31 | -0.39 | -0.46 | -0.52 | -0.58 | -0.76 | -0.85 | -0.88 | -0.88 | -0.85 |
| Percentage-point | |||||||||||
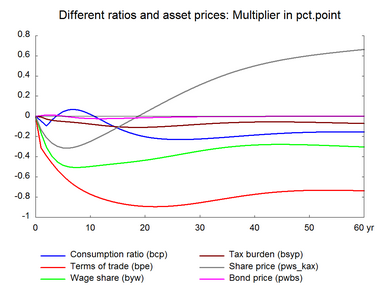
| Consumption ratio | bcp | -0.05 | -0.09 | -0.04 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.02 | -0.12 | -0.20 | -0.23 | -0.22 |
| Wage ratio | byw | -0.17 | -0.31 | -0.40 | -0.45 | -0.48 | -0.50 | -0.47 | -0.43 | -0.39 | -0.34 |
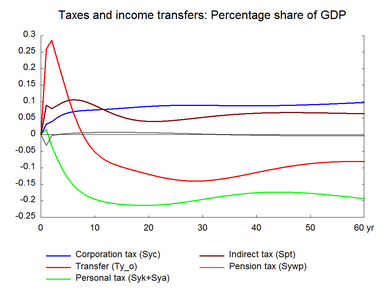
As the amount of output demanded can be produced by less labor, employment falls already in the first year, and due to lags in the labor demand relation the negative effect on employment peaks in the second year. The lower employment reduces wage growth and hence prices and unit costs fall relative to the baseline. Falling prices improve competitiveness so exports and production increase. Over time employment peaks and then returns to the baseline.
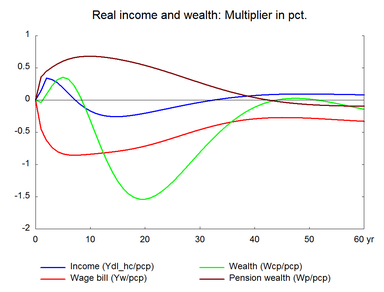
Compared to the previous two experiments - increase in the number of workers and the working hours, nominal hourly wages fall relatively by a smaller percentage when labor efficiency improves, because production costs fall and make producer prices fall. Therefore, nominal wages do not have to decrease substantially to induce a fall in prices, as in the cases of longer working hours or in particular a larger labor force. Consequently, net exports increase and offset some of the initial fall in labor demand. This also explains the stronger response in exports in the present experiment. Moreover, in the long run there is only a small negative effect on real hourly wages.
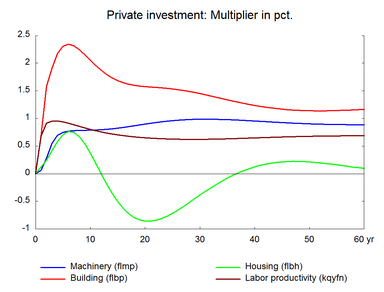
Investments in machinery fall as the improvement in labor efficiency leads to the substitution of labor for machinery. Capital intensity of production falls as production involves less capital and more labor. Due to this fall in capital intensity, output per working hour increases by less than 1 per cent despite the 1 per cent increase in labor efficiency. There is no effect on private consumption in the long run.
Note the higher unemployment in the short run raises unemployment benefits and worsens public finance temporarily. Later on the initial worsening in the government budget is reversed and continues to be positive as employment rises and tax revenues increase. The improved competitiveness also enhances the balance of payment.
Figure 12. The effect of a permanent 1 per cent increase in labor efficiency